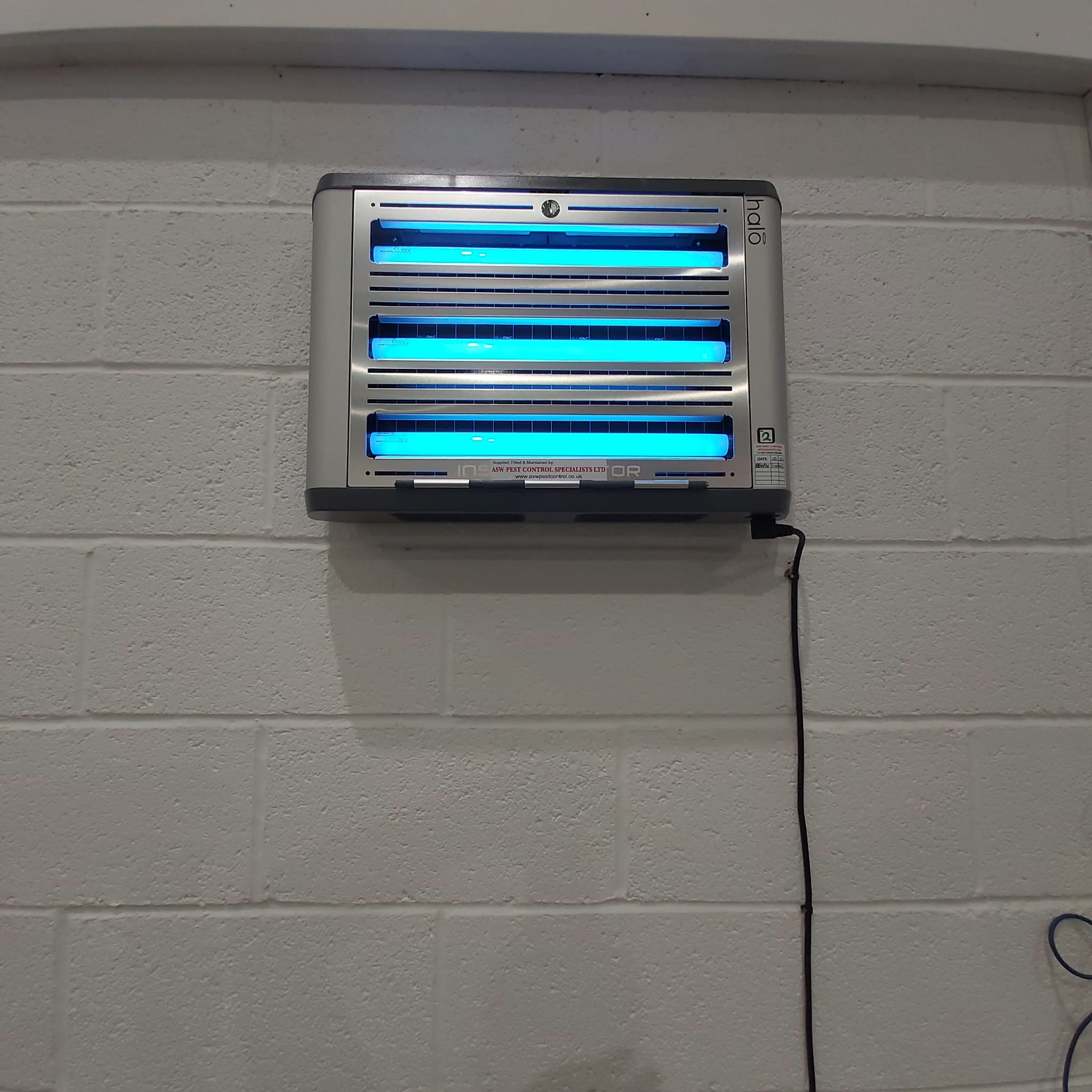
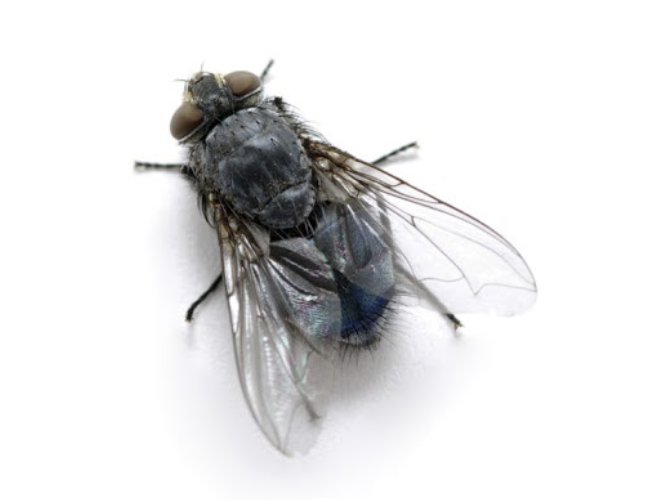
Cluster Flies, Common House Flies, Blowflies (Bluebottle & Greenbottle), Fruit Flies, Sewage Flies


You can either call us on 0800 592011 or fill out our simple contact form.

One of our pest control experts will call you or reply via email to arrange the appointment instantly.

ASW'S technician will carry out the required visits and we will be at the end of the phone if you need us.

There are more than 100,000 different species of fly across the world, all of which are incredibly advanced in evolutionary terms. They are often seen as dirty insects with distasteful habits, which is mostly true of many of the species closely associated with humans.

There are more than 100,000 different species of fly across the world, all of which are incredibly advanced in evolutionary terms. They are often seen as dirty insects with distasteful habits, which is mostly true of many of the species closely associated with humans.
Cluster flies are found throughout the Uk and Europe. They are called cluster flies due their habit of gathering in sometimes very large numbers for hibernation in buildings. These buildings will often be used year after year.
Adult cluster flies spend the summer outdoors and are of no concern. Once temperatures begin to drop in autumn they will enter buildings, usually loft voids and window frames, to hibernate.
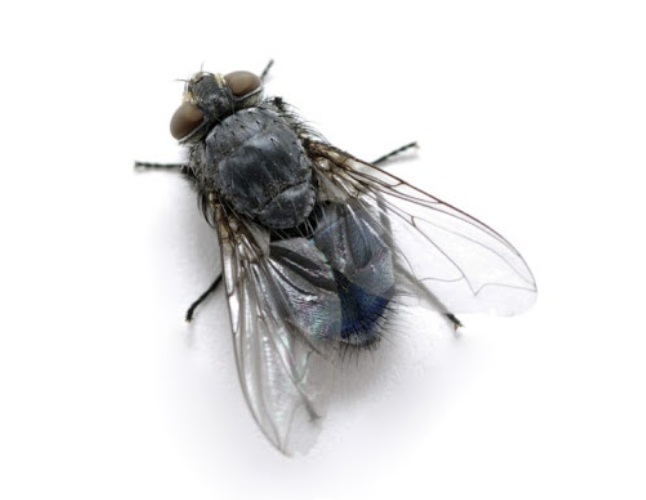

The house fly is found wherever suitable breeding conditions exist, usually rotting/fermenting or at least moist organic matter with high protein content preferable. They are frequently found in association with humans either indoors or taking advantage of other human activities.
Female common house flies lay large batches of eggs, up to 150 at one time, onto suitable food for the resulting larvae and, depending on the rotting or fermenting level of this substrate, larvae will hatch from 8 to 48 hours after eggs being laid.
Houseflies are known transmitters of enteric diseases and intestinal parasitic worms and have been implicated in the spread of typhoid and cholera. They form an unwelcome intrusion into domestic properties and are indiscriminate in types of food material on which they settle and feed.
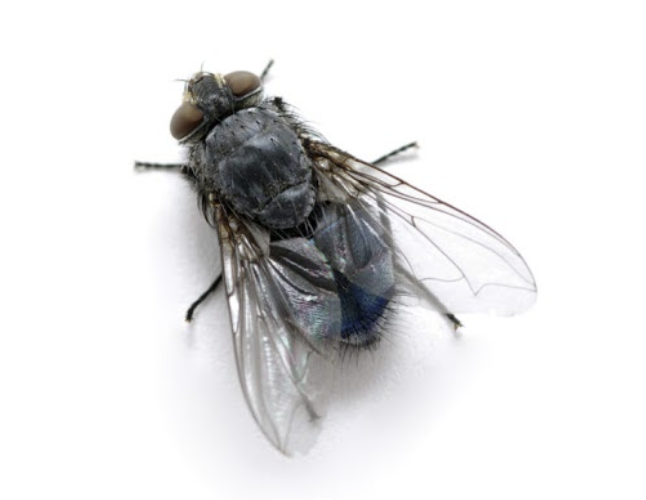

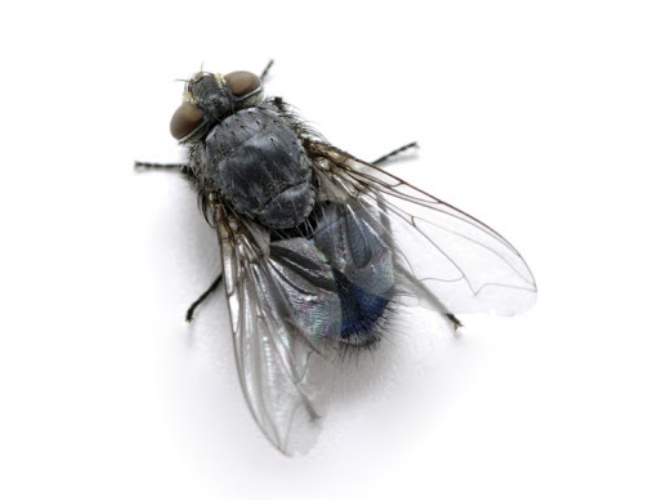
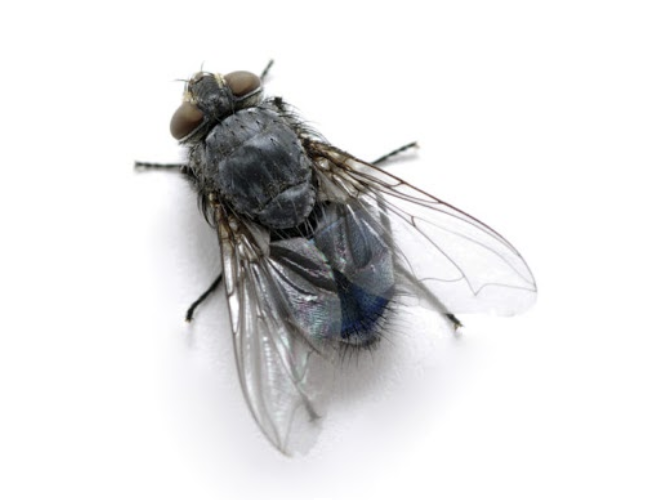
The bluebottle primarily breeds on dead and decaying animal matter, preferably carcasses or meat offal. They are incredibly common in the wild and frequently associated some human activities.
Adult bluebottles will mate and after 4 or 5 days start producing and laying eggs. In domestic and food factories this is called “blowing”, the depositing of eggs in large clusters on fresh or older meat, meat products and offal or even on excrement. The extraordinarily acute sense of smell of the adult female fly helps them single out freshly killed animals and game birds.
In countryside environments, blowflies carry out a valuable role in helping the removal and recycling of dead animals and birds. However, in human establishments, they can cause significant problems as they can carry disease and there presence on foodstuffs can render foods unfit for human consumption.

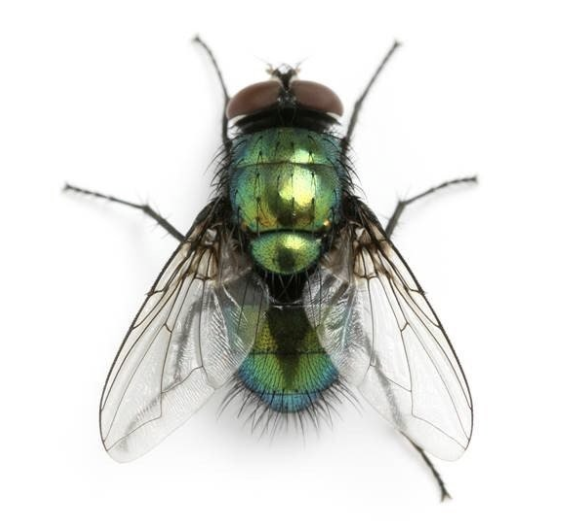
Green Bottles are very similar to bluebottle in their breeding rates and activities though are smaller and easily identified by their bright metallic green bodies. Green Bottles are seldom attracted indoors and can often be seen sunning themselves on fence posts and house walls. They rely much more on dead bodies of animals and excrement for breeding and feeding sites.

The fruit fly is a relatively small insect compared with some of the other fly species. They have a fondness of fermenting material, preferably of fruit origin, and can often be found feeding of sap exuding from trees and rotting fruit on the ground.
Whilst they can venture indoors if human activity produces attractive conditions, they are mainly an out of doors species. They have a high breeding rate in high temperatures, with females laying up to 25 eggs per day moving through larval stages quickly and adult flies emerging within 7 or 8 days at temperatures of around 30 degrees.
Whilst out of doors, they are rarely a concern for humans though infestations developing in picking or fruit packaging plants or in refuse areas of kitchens and canteens the clouds of adults are a nuisance. The habit of some fruit flies of feeding on faeces and other excrement before settling on clean materials such as food prep areas makes them totally unacceptable.

Sewage flies are a very small species and are commonly found around sewage treatment plants. Feeding and breeding within the filter beds, numbers can rise quickly during warmer months.
Their development within the environs of sewage treatment plants means that adults can potentially transmit a variety of disease organisms and their presence in large swarms getting into eyes, mouths and noses makes them a considerable nuisance for workers and local residents during the summer months.